How Many Babies Does One Pint of Blood Help
Blood is a specialized torso fluid. It has four main components: plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Blood has many different functions, including:
- transporting oxygen and nutrients to the lungs and tissues
- forming blood clots to prevent excess blood loss
- conveying cells and antibodies that fight infection
- bringing waste matter products to the kidneys and liver, which filter and clean the blood
- regulating body temperature
The blood that runs through the veins, arteries, and capillaries is known as whole blood, a mixture of almost 55 percent plasma and 45 percent claret cells. About 7 to 8 percent of your total body weight is blood. An average-sized man has nearly 12 pints of claret in his body, and an average-sized woman has nearly nine pints.
The Components of Claret and Their Importance
Many people have undergone blood tests or donated blood, merely hematology - the study of blood - encompasses much more than this. Doctors who specialize in hematology (hematologists) are leading the many advances being made in the treatment and prevention of blood diseases.
If you or someone y'all intendance about is diagnosed with a claret disorder, your primary care physician may refer you to a hematologist for further testing and treatment.
Plasma
The liquid component of blood is called plasma, a mixture of water, sugar, fat, poly peptide, and salts. The master job of the plasma is to send claret cells throughout your body forth with nutrients, waste products, antibodies, clotting proteins, chemic messengers such as hormones, and proteins that help maintain the body's fluid residuum.
Red Blood Cells (as well chosen erythrocytes or RBCs)
Known for their bright red colour, red cells are the most abundant jail cell in the claret, accounting for almost xl to 45 percent of its volume. The shape of a red blood cell is a biconcave disk with a flattened center - in other words, both faces of the disc have shallow bowl-like indentations (a red blood cell looks like a donut).
Production of red blood cells is controlled by erythropoietin, a hormone produced primarily by the kidneys. Red blood cells start as young cells in the bone marrow and after approximately seven days of maturation are released into the bloodstream. Unlike many other cells, red claret cells have no nucleus and can easily alter shape, helping them fit through the various blood vessels in your trunk. Even so, while the lack of a nucleus makes a red blood jail cell more flexible, it also limits the life of the cell as it travels through the smallest blood vessels, damaging the prison cell'due south membranes and depleting its energy supplies. The red claret prison cell survives on average but 120 days.
Red cells contain a special protein chosen hemoglobin, which helps carry oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body and so returns carbon dioxide from the body to the lungs so it tin be exhaled. Blood appears ruddy because of the large number of red blood cells, which get their colour from the hemoglobin. The percent of whole blood volume that is made up of red blood cells is called the hematocrit and is a common mensurate of red claret cell levels.
White Claret Cells (likewise called leukocytes)
White claret cells protect the body from infection. They are much fewer in number than red blood cells, accounting for about 1 pct of your blood.
The nearly mutual blazon of white claret prison cell is the neutrophil, which is the "immediate response" cell and accounts for 55 to 70 percent of the total white claret cell count. Each neutrophil lives less than a 24-hour interval, so your bone marrow must constantly brand new neutrophils to maintain protection confronting infection. Transfusion of neutrophils is generally non constructive since they practice not remain in the body for very long.
The other major type of white blood cell is a lymphocyte. There are two primary populations of these cells. T lymphocytes assist regulate the office of other immune cells and directly attack various infected cells and tumors. B lymphocytes make antibodies, which are proteins that specifically target leaner, viruses, and other foreign materials.
Platelets (likewise called thrombocytes)
Unlike carmine and white blood cells, platelets are not actually cells but rather pocket-size fragments of cells. Platelets aid the blood clotting process (or coagulation) by gathering at the site of an injury, sticking to the lining of the injured claret vessel, and forming a platform on which blood coagulation can occur. This results in the formation of a fibrin jell, which covers the wound and prevents blood from leaking out. Fibrin likewise forms the initial scaffolding upon which new tissue forms, thus promoting healing.
A higher than normal number of platelets tin crusade unnecessary clotting, which can atomic number 82 to strokes and centre attacks; however, thanks to advances made inantiplatelet therapies, there are treatments available to help prevent these potentially fatal events. Conversely, lower than normal counts can lead to all-encompassing haemorrhage.
Consummate Blood Count (CBC)
A consummate blood count (CBC) examination gives your physician important data nigh the types and numbers of cells in your blood, especially the crimson blood cells and their percentage (hematocrit) or poly peptide content (hemoglobin), white blood cells, and platelets. The results of a CBC may diagnose conditions similar anemia, infection, and other disorders. The platelet count and plasma clotting tests (prothombin time, fractional thromboplastin time, and thrombin time) may be used to evaluate bleeding and clotting disorders.
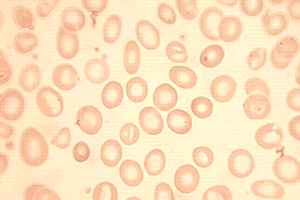
Your doc may too perform a blood smear, which is a way of looking at your blood cells nether the microscope. In a normal blood smear, cherry-red blood cells will appear equally regular, round cells with a pale eye. Variations in the size or shape of these cells may suggest a blood disorder.
Where Exercise Blood Cells Come up From?
Claret cells develop from hematopoietic stem cells and are formed in the bone marrow through the highly regulated process of hematopoiesis. Hematopoietic stem cells are capable of transforming into red claret cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These stem cells can be found circulating in the blood and bone marrow in people of all ages, as well every bit in the umbilical cords of newborn babies. Stem cells from all iii sources may be used to treat a diversity of diseases, including leukemia, lymphoma, bone marrow failure, and diverse allowed disorders.
Where Can I Find More Data?
If y'all are interested in learning more about blood diseases and disorders, hither are a few other resource that may exist of some help:
Articles From Hematology, the ASH Education Program Book
The American Society of Hematology (ASH) Educational activity Book, updated yearly by experts in the field, is a drove of manufactures about the current treatment options bachelor to patients. The articles are categorized here by illness type. If you lot are interested in learning more than about a item blood affliction, we encourage you to share and discuss these manufactures with your doctor.
Results of Clinical Studies Published in Claret
Search Blood, the official journal of ASH, for the results of the latest blood research. While recent articles generally require a subscriber login, patients interested in viewing an access-controlled article in Blood may obtain a copy by e-mailing a request to the Claret Publishing Office.
Patient Groups
This department includes a list of Web links to patient groups and other organizations that provide information.
Source: https://www.hematology.org/education/patients/blood-basics
0 Response to "How Many Babies Does One Pint of Blood Help"
Post a Comment